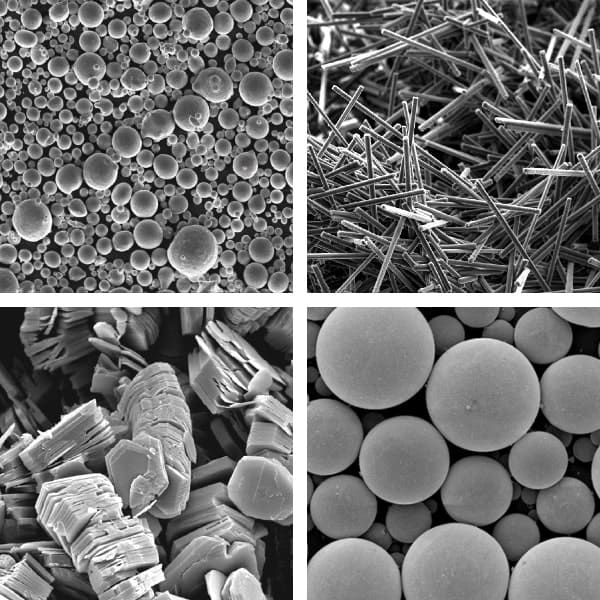
Summary of the use of fillers & reinforcing agents
Fillers improve many properties that the polymeric material does not have or cannot achieve on its own. In particular, they can achieve one or more of the following effects:
- increased stiffness and hardness;
- regulation of thermal expansion and shrinkage;
- increase in thermal resistance;
- reduction of creep;
- modification of rheological properties (flow, thixotroy);
- easier implementation;
- modification of the appearance (opacity, color, texture).
These tables present the characteristics of the most commonly used mineral fillers and the different properties provided by these products and the recommended rates.
Physico-chemical properties of the main mineral fillers
| CaCO3 | Silices | Talcs | Wollastonite | Clay (kaolin) | Mica | Al(OH)3 | Glass beads | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constituting water | < 2,0 % | < 0,1 % | 4,8 % | 0,5 % | < 0,5 % | < 5,0 % | 34,6 % | < 0,1 % |
| Density | 2,60 à 2,75 | 2,65 | 2,7 à 2,8 | 2,9 | 2,5 | 2,74 à 2,95 | 2,42 | 2,48 |
| Hardness Mohs | 3,0 | 7,0 | 1,0 | 4,5 | 4,0 à 6,0 | 2,4 à 3,0 | 2,5 à 3,5 | 5,5 |
| Melting or decomposition temperature (°C) | 900 | 573 | 380 | 1 540 | 1 810 | 1 300 | 200 à 600 | 1 200 |
| Refractive index | 1,49 | 1,55 | 1,59 | 1,63 | 1,56 | 1,54 à 1,69 | 1,58 | 1,51 |
| Color | white | white | grey white | white | white | gold, brown or white | white | colourless |
| Shape | granular prismatic | spherical | lamellar | acicular | lamellar | lamellar | lamellar | spherical |
| Moisture content | < 0,2 % | < 0,1 % | < 0,3 % | < 0,2 % | < 0,5 % | < 0,3 % | < 0,3 % | < 0,1 % |
Properties and use of the main fillers in thermoplastics
Natural organic products| Type of loads | Properties | Incorporation rate (% by mass) |
|---|---|---|
| Wood flour | Reduces shrinkage during molding. Provides good electrical properties and shock resistance. |
4 to 5 |
| Fruit peel flour | Improves flow as well as shine. Decreases water absorption. |
4 to 5 |
| Starch | Allows obtaining biodegradable materials. | 7 |
Synthetic organic powders
| Type of loads | Properties | Incorporation rate (% by mass) |
|---|---|---|
| Styrene/butadiene elastomer | Increases shock resistance. | 1 to 2 |
| PTFE and fluorinated polymers | Improves shock resistance and lubrication. | 1 to 2 |
| Cellulose acetate butyrate | Reduces shrinkage during molding. | 1 to 2 |
| Polyethylene | Improves surface finish. | 1 to 2 |
Carbon
| Type of loads | Properties | Incorporation rate (% by mass) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Black | Ultraviolet stabilizer. Facilitates cross-linking. | up to 50x (in volume) |
| Graphite | Improves stiffness and creep resistance. | up to 50x (in volume) |
| Petroleum Coke | Improves tensile strength and heat resistance. | up to 50x (in volume) |
| Hollow carbon spheres (carbospheres) | Lower the density. | 30 to 50 (in volume) |
Metals
| Type of loads | Properties |
|---|---|
| Aluminium, steel, copper, zinc, nickel, bronze. | Improves heat resistance and electrical conductivity. |
Metal oxides
| Type of loads | Properties |
|---|---|
| Aluminum oxide | Improves fire resistance. |
| Magnesium oxide | Increases the viscosity of the premixes, as well as the hardness and rigidity of the parts. |
| Zinc oxide | Increases electrical conductivity and resistance to ultraviolet rays. |
| Beryllium oxide | Increases electrical conductivity. |
| Aluminium, steel, copper, zinc, nickel, bronze. | Improves heat resistance and electrical conductivity. |
Silicas
| Type of loads | Properties |
|---|---|
| Silica sands | Reduce shrinkage during molding. |
| Quartz | Improves moisture resistance and resistance to cracking. |
| Diatomaceous earth flour (tripoli) | Increases the compressive strength of foam products. Improves thermal, electrical and sound insulation. |
| Thermal silica (or pyrogenation) | Increases viscosity, improves thixotropy. |
Silicates
| Type of loads | Properties | Incorporation rate (% by mass) |
|---|---|---|
| Talcs | Provides white to light gray pigmentation. Improves flow. Increase the rigidity of the parts. |
|
| Micas | Increase the rigidity and hardness of the parts. Facilitate demolding. |
> 25 |
| Kaolin | Improves molding. | 20 to 45. |
| Wollastonite | Reduces water absorption. Improves shock resistance and thermal and dielectric properties. |
1 to 50 |
| Glass (microspheres) | Increases Young's modulus in compression. Facilitates mold filling. |
10 to 40 |
Other mineral powders
| Type of loads | Properties | Incorporation rate (% by mass) |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium carbonate | Improves gloss as well as mechanical resistance. Facilitates extrusion. |
5 à 33 |
| Potassium Titanate | Improves dimensional stability and reduces the molding cycle. | 40 |
| Barium Sulfate | Increases density and compressive strength. | 10 à 25 |
| Barium ferrite | Gives magnetic properties. | up to 90 |
Let’s dive into the possibilities offered by PAM
From pellets to object, PAM technology offers the most direct process to high performances end-parts.
Metals Ceramics Commodity Elastomers Performance High Performance.





Newsletter
sign up for updates
We’ll never share your email address with anyone.
And you can opt out at any time. We promise.

© 2026 Pollen AM inc. All rights Reserved.




