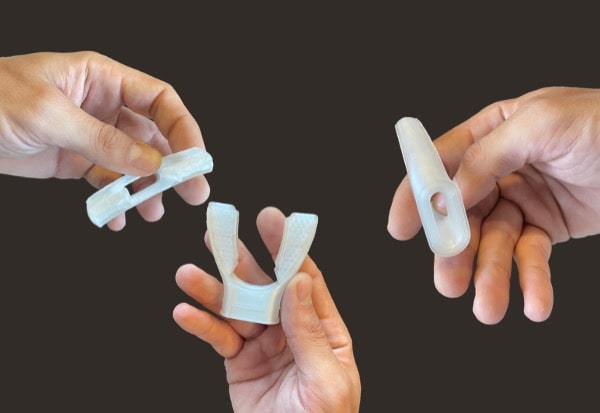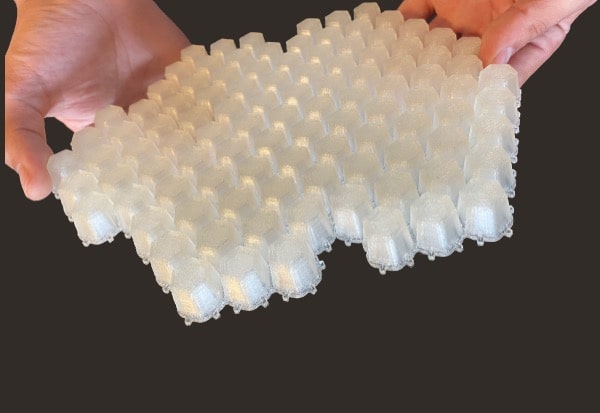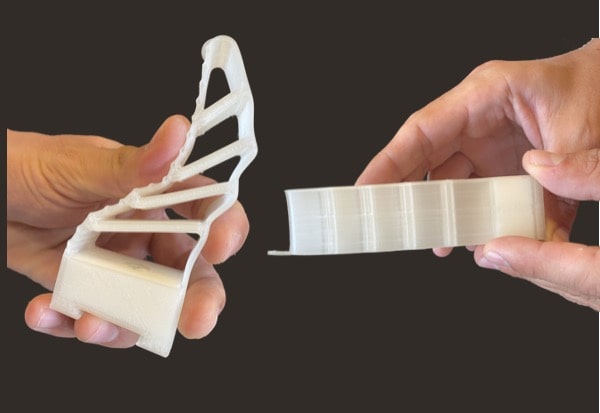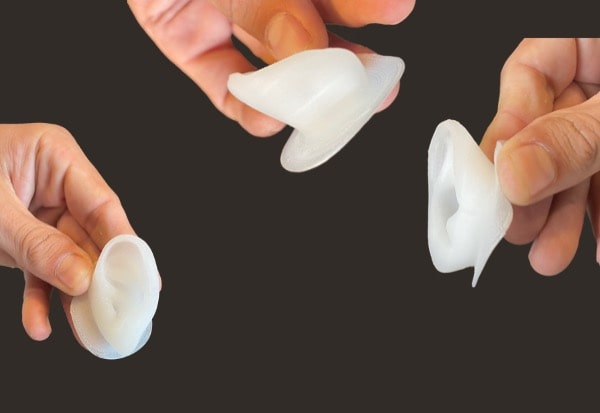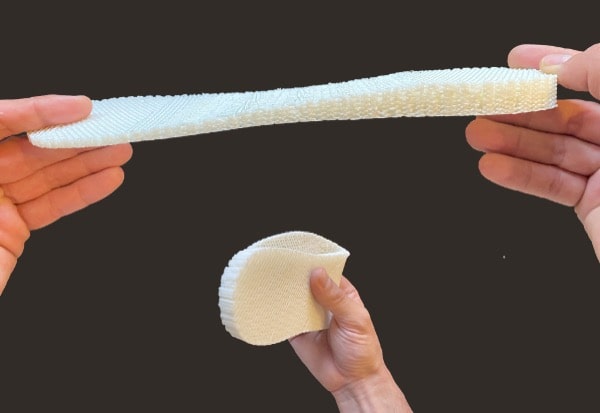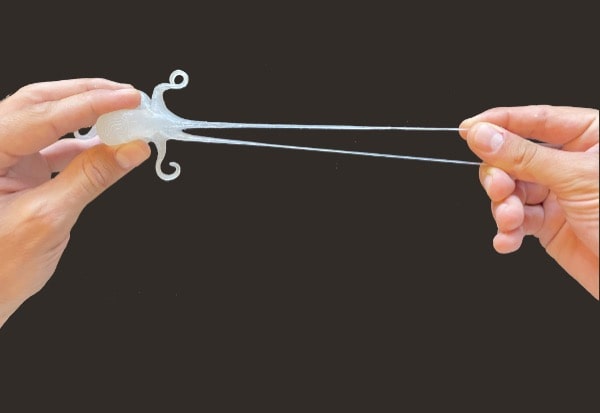
Thermoplastics elastomers
Flexible materials for flexible applications.
Elastomer is the family of all the thermoplastics that present flexible properties. Hardness is used to measure this property on each material, and expressed in shore durometer.
Using standard thermoplastic elastomers with Pam 3D printers particularly makes sense for industrial already used to them but especially when you the application requires the use of TPE from hardness inferior to 70 shore A, where other 3D printing technologies can't.
Existing grades can be printed as-is at their unbeatable high volume price.
The power of pellets is particularly visible here as the Pam Technology can treat materials without any hardness limit. Moreover, an isotropic behavior of these materials has been demonstrated when treated by the Pam Technology.
According to ISO 18064 standard commercial TPE's are classified into six generic classes:
- Styrenic block copolymers, TPS (TPE-s)
- Thermoplastic polyolefin elastomers, TPO (TPE-o);
- Thermoplastic Vulcanizates, TPV (TPE-v or TPV);
- Thermoplastic polyurethanes, TPU (TPU);
- Thermoplastic copolyester, TPC (TPE-E);
- Thermoplastic polyamides, TPA (TPE-A).
Examples of TPE materials that come from block copolymers group are amongst others CAWITON, THERMOLAST K, THERMOLAST M, Arnitel, Hytrel, Dryflex, Mediprene, Kraton, Pibiflex, Sofprene, and Laprene.
In order to qualify as a thermoplastic elastomer, a material must have these three essential characteristics:
- The ability to be stretched to moderate elongations and, upon the removal of stress, return to something close to its original shape;
- Processable as a melt at elevated temperature;
- Absence of significant creep.
Thermoplastic material classification
From standard to high-performance thermoplastics.
Pam 3D printers are dedicated to industrial materials with thermoplastic behavior treatment; from injection moulding thermoplastics to PIM feedstocks.
Thermoplastics are usually classified into different categories according to their polymer families and their temperature resistance.
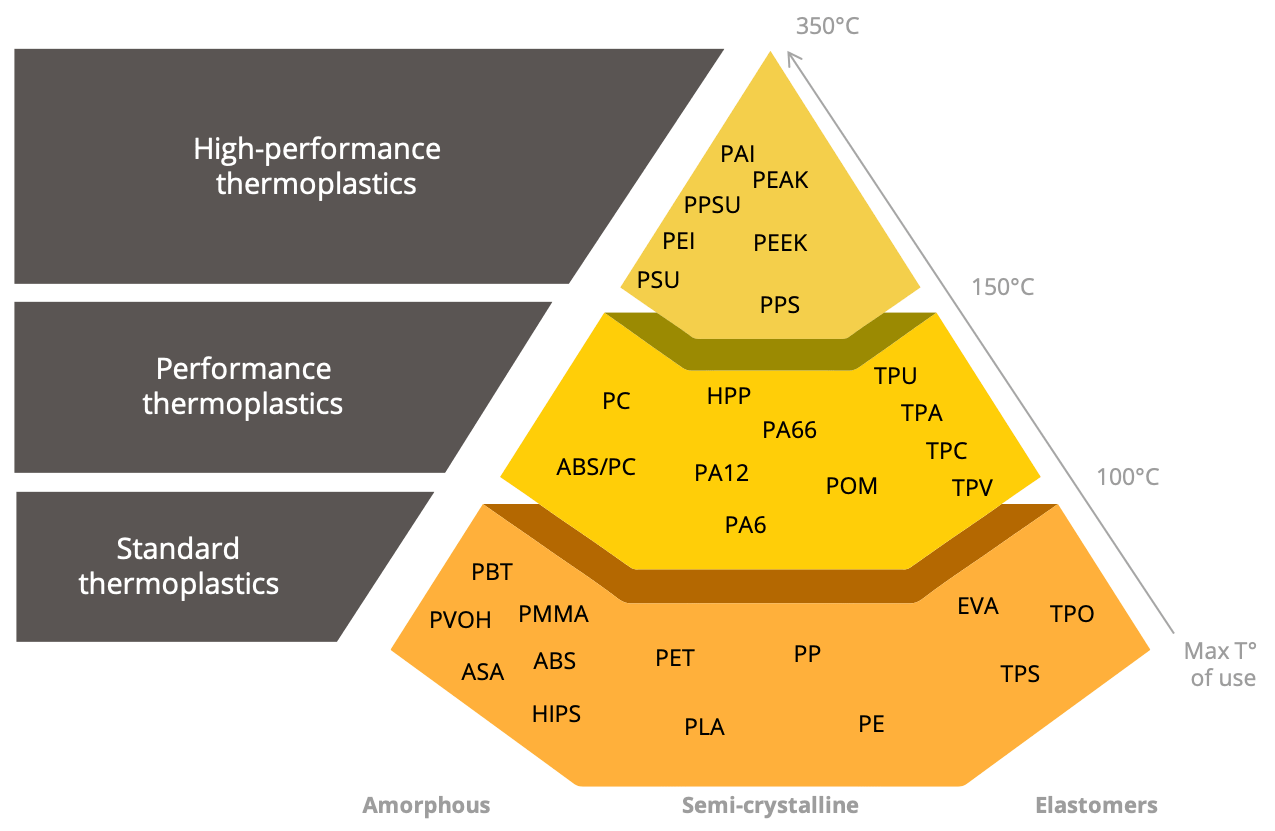
There are three polymer families: amorphous, semi-crystalline and elastomers, they are subdivided into three thermal categories : standard materials, performance materials and high-performance materials.
Thermoplastics with an amorphous structure are generally transparent and tend to be less sensitive to crack propagation (higher toughness). Due to their high-dimensional stability, they are suitable for precision parts.
Semi-crystalline thermoplastics are generally opaque, rigid and have good chemical resistance.
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) are a category in their own right due to their heterogeneous structure consisting of flexible and rigid domains, they are located halfway between crosslinked elastomers and thermoplastics.
As a dedicated technology inspired by micro-extrusion techniques, the Pam Technology is meant to 3D print most kinds of thermoplastic polymers.
Discover 3D printed parts with Pam