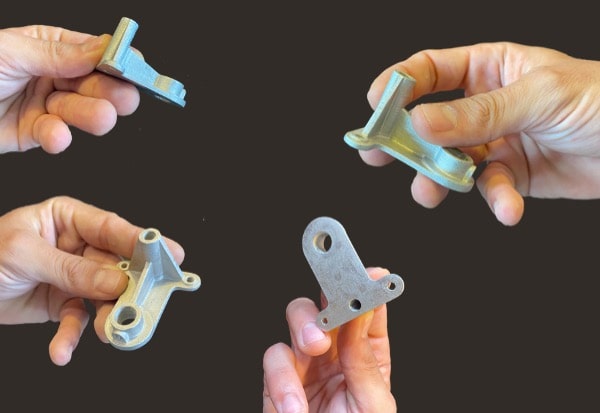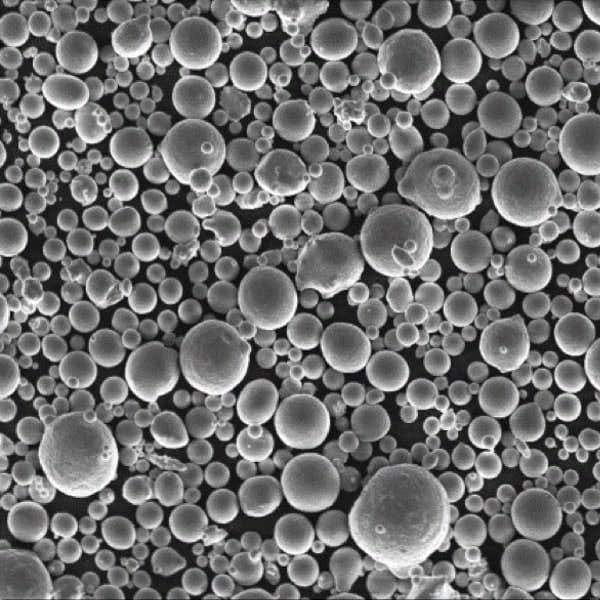
Metallic fillers
The addition of metallic powders or flakes (aluminum, copper, nickel, iron, etc.) is carried out to make plastic materials used in aerospace, electronics (enclosures) conductive of electricity or heat, particularly for the electromagnetic protection of various devices.
Aluminum: improves machinability, shock resistance, thermal and electrical conductivity. It is used in tool parts, paints, experimental synthetic paper, cold plastic welding.
Copper: improves machinability, thermal and electrical conductivity. It is used in tooling, decoration (such as bronze).
Iron: improves abrasion resistance.
Lead: of high density provides protection against corrosion, radiation and sound absorption in high density materials.
Stainless steel is used in tooling.
Zinc improves corrosion resistance and is used in protective coatings.
The introduction of metallic powders, e.g. aluminium or bronze, makes it possible to obtain conductive thermoplastic parts, which can be plated with metals.
Metallic flakes of varying sizes are now available, ranging from 15 to 380 μm, with a minimum thickness of 0.33 μm. Some are magnetic (nickel and stainless steel).
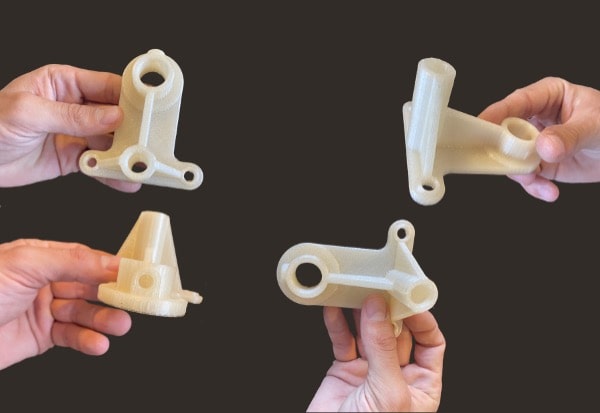
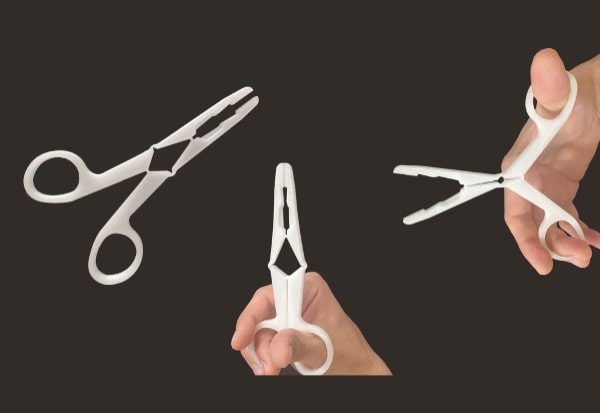
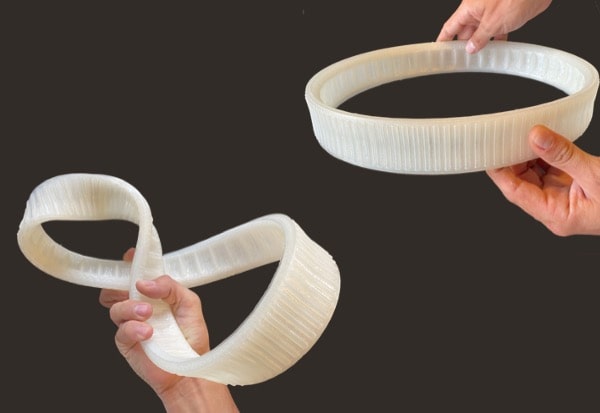
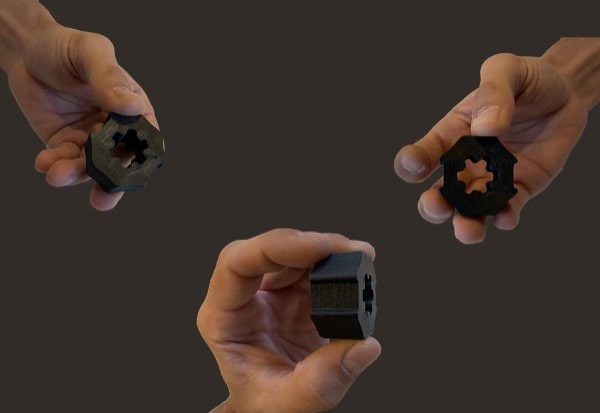
Let’s dive into the possibilities offered by PAM
From pellets to object, PAM technology offers the most direct process to high performances end-parts.
Metals Ceramics Commodity Elastomers Performance High Performance.





Newsletter
sign up for updates
We’ll never share your email address with anyone.
And you can opt out at any time. We promise.

© 2026 Pollen AM inc. All rights Reserved.