Design guidelines
Digital manufacturing process.
PAM technology (acronym for Pellet Additive Manufacturing) is an additive manufacturing process of the FDM type using thermoplastic pellets as raw material.
Truly open to industrial materials, the PAM technology makes it possible to dispense with filaments, powders, liquid resins or any other format specific to additive manufacturing.
Offering the advantage of using raw materials at the lowest cost on the market, PAM technology opens up a virtually infinite library of compatible materials while benefiting from the available material certificates (skin contact, food contact, smoke fire, etc.).
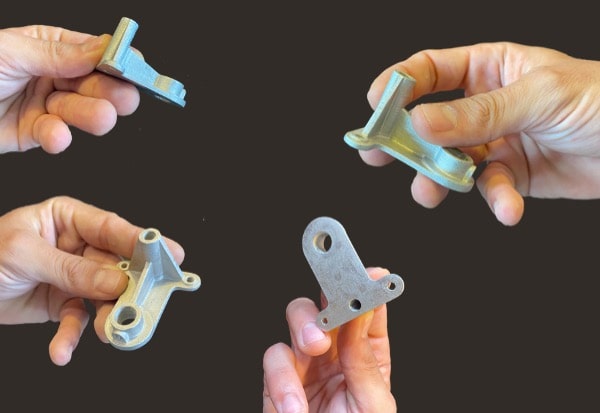
It is now possible to produce prototypes, tools, templates, parts in small and medium series using the same material as in injection molding, without investing in specific tooling.
PAM technology allows the manufacture of parts from thermoplastic, metallic and ceramic materials by successive addition of layers.
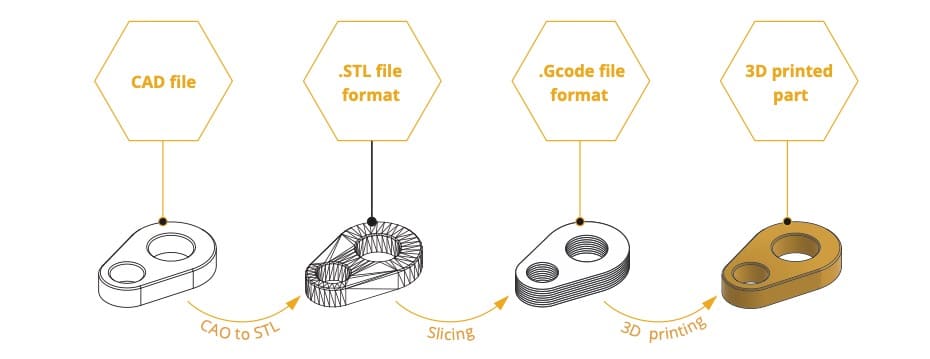
Digital manufacturing process
Like all digital manufacturing processes, the PAM process can be represented by its production line, which includes all the digital and physical transformations that go from a CAD model to a printed object.
The PAM manufacturing chain is divided into four steps:
- 3D modelling through a CAD software;
- The encoding of the surface geometry of the CAD model (conversion to .STL format, etc.);
- The interpretation of the obtained file by a "Slicing" software to obtain a G-Code;
- The execution of the command file by the PAM additive manufacturing system.
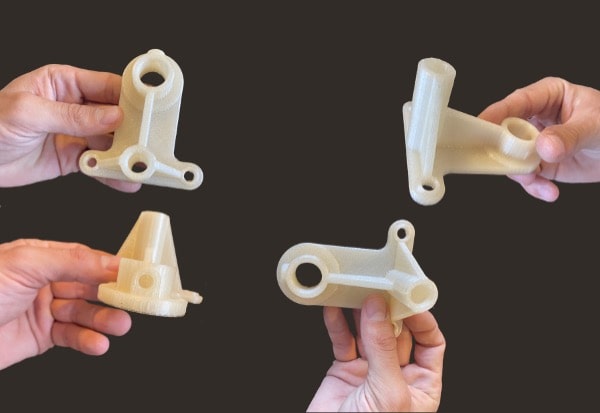
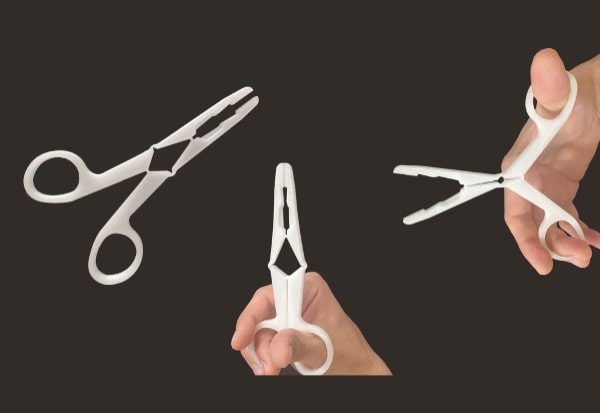
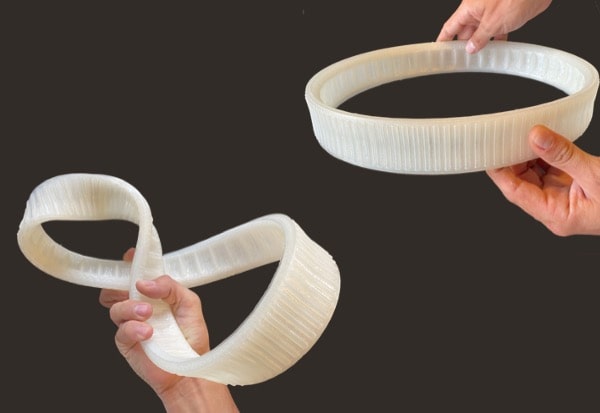
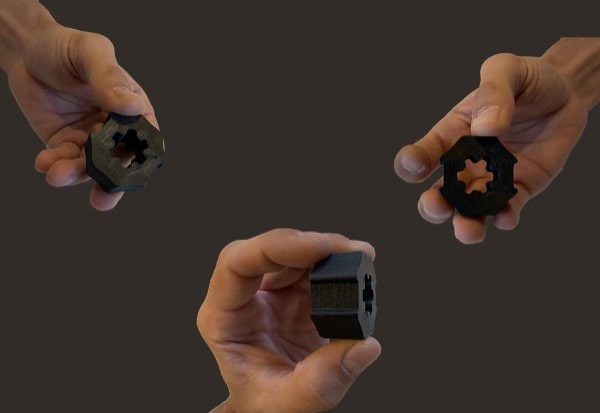
Let’s dive into the possibilities offered by PAM
From pellets to object, PAM technology offers the most direct process to high performances end-parts.
Metals Ceramics Commodity Elastomers Performance High Performance.










