Pellet shapes material
Industrial reference
Plastic resin pellets are small granules generally with shape of a cylinder or a small sphere with a diameter of a few millimeters.

These plastic elements are industrial raw material references. This is one of the most efficient storage and transportation format. Every plastic manufacturing industry uses pellet shape materials to produce final parts. Other names for this material include pre-production plastic, nurdles and granules.
Pellet shape thermoplastics are obtained by different industrial processes such as chemical reaction, cracking process, polymerization reactions, refined processes, etc.
To improve the resins some compounding activities can be operated (adding plasticizers, colours, and flame-resistant chemicals, reinforcing agent, etc.).
Pollen AM decides to develop an industrial 3D printing technology to allow manufacturers to produce parts with material they already work with!
Why using 3D printing with pellets shapes material?
Most 3D printing technologies on the market come with a specific material format: filaments for fused deposition modelling, resins for stereolithography and powders for sintering. The vision spread by this concept is to highlight a technology and then propose a compatible material catalogue.
This approach is similar to that of paper printer manufacturers who offer cartridge formats specific to their system to keep control over consumables and optimize the profitability of their product.
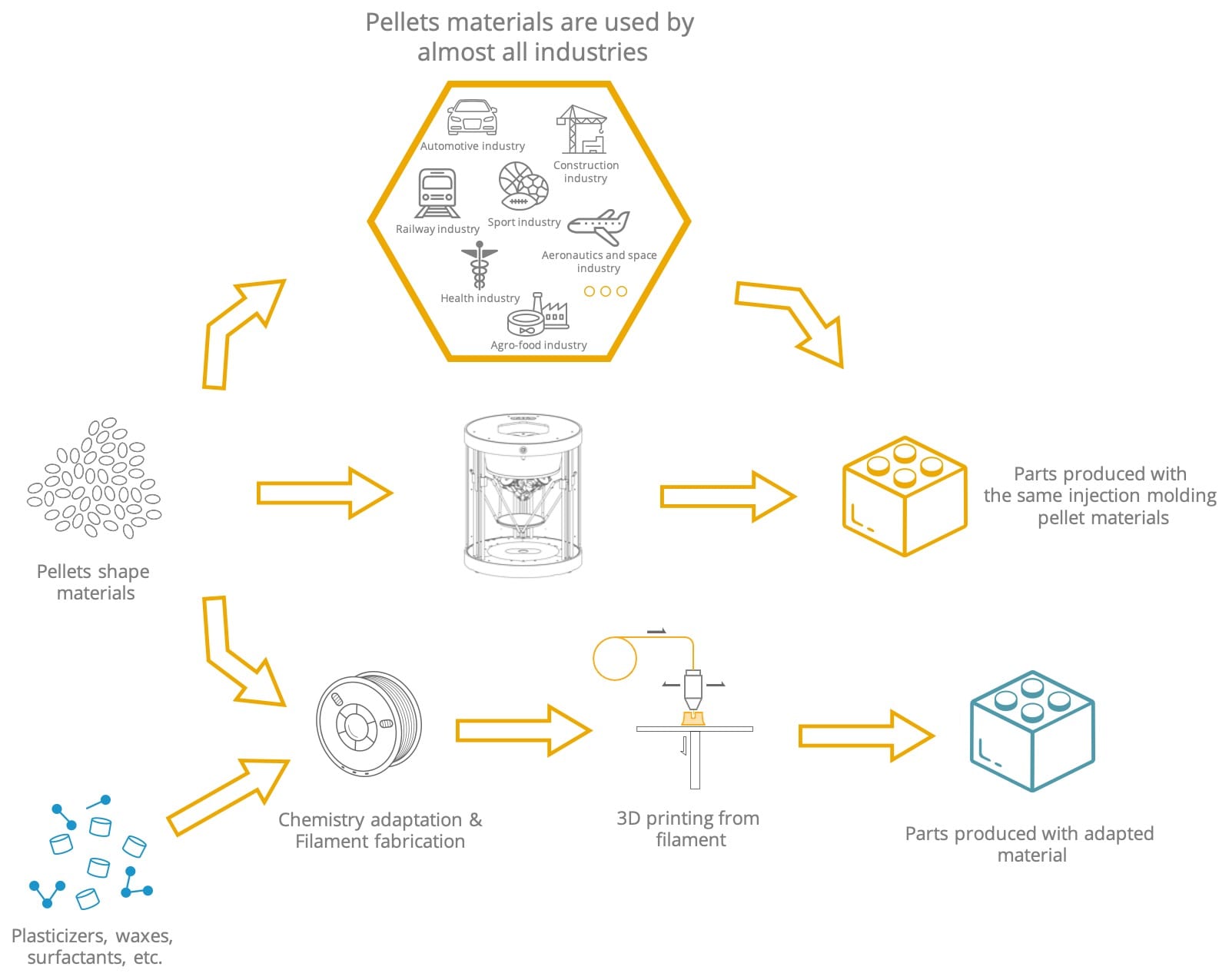
Pollen AM's vision is different because we developed Pam technology with the goal of giving users complete freedom over which materials they want to process and how they want to source them. Pollen AM provides a complete service to support its user during their own development.
Pam systems are therefore open systems that do not require a specific format but, on the contrary, adapt to the most widespread material format in the world: thermoplastic pellets.
We see several advantages with the use of pellet materials in an open system :
- material cost;
- the most innovative and complete material portfolio on the market;
- a robust supply chain;
- a freedom of formulation.
Material cost
Pellets take advantage of an industrial production volume to offer the most competitive prices on the market.
| Pam | FFF | SLA | SLS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material format | Industrial pellets | Proprietary or open filaments | Resin | Powder |
| ABS | Wholesale: 2 - 5 €/Kg Retail: 5 - 10 €/Kg |
Retail: 15 - 25 €/Kg | Not available Retail: ABS-Like : 160 €/L |
Not available |
| PC | Wholesale: 4 - 7 €/Kg Retail: 10 - 15 €/Kg |
Retail: 60 - 90 €/Kg | Not available | Not available |
| TPE | Wholesale: 5 - 7 €/Kg Retail: 10 - 20 €/Kg |
Retail: 80 - 90 €/Kg Hardness > 70 ShA |
Retail: 190 €/L | Retail: 192 €/Kg Hardness > 70 ShA |
| PEEK | Wholesale: 50 - 70 €/Kg Retail: 80 - 100 €/Kg |
Retail: 450 - 650 €/Kg | Not available | Not available |
The most innovative and complete material portfolio on the market
Pam's compatibility with pellet shape materials offer the most complete and innovative material catalogue on the market.
While specific formats for 3D printing require users to have a high level of need before they can offer a material in its specific format, pellets offer a complete catalogue immediately.
A Pam system opens the door to 3D printing for materials that are not currently part of the additive manufacturing market standard.
Moreover, the use of granules allows you to directly use approved or certified materials for specific applications: skin or food contact, fire, smoke or medical standards.
A robust supply chain
The use of pellets allows you to benefit from a mature industry with proven logistics and a wide choice of suppliers.
Working with pellets minimizes supply risks by working directly in the standard format.
It is interesting to note, for example, that the attraction of bio-sourced materials, including PLA, from major industries is putting a strain on the availability of these materials, which is detrimental to 3D filament printing. Indeed, since 3D printing represents a small share of the world's material consumption compared to large industries, the risk of shortages or price increases is particularly high.
Pollen AM has been working since its beginnings with the world's major material producers to demonstrate the adaptability of its systems and to benefit from the expertise of its customers.
Freedom of formulation
The pellet market is particularly mature and offers a wide range of contacts.
From major world producers to compounders and colorists, granules have a strong potential for innovation and variety in formulations.
You can thus easily develop a formulation specific to your activity, a unique coloring or use recycled materials easily and autonomously.
Compatibility with existing means: injection, extrusion, rotomolding
Pellet materials are widely used in the plastic industry.
Some of the more popular uses of resin pellets include the following:
Injection molding: During the injection molding process, pellets are heated and then placed within a chamber for mixing. Through the use of high pressure, the melted mixture is then put within a mold to shape a part.
Extrusion: During the extrusion process, resin pellets are heated and placed within a chamber. Following this, the material is put through a small opening for cooling by way of either water or air.
Rotational molding: The pellets are heated and then cooled down within a mold that has the ability to be rotated three dimensionally. Because of the rotation, the plastic is distributed evenly within the mold, covering its walls. Oversized, hollow plastic items are often crafted by way of this process, including such products as children’s toys, sporting goods, trash cans, etc.
Blow molding: Both injection and extrusion molding play a role with blow molding. During the process, the selected resin pellets are heated and then compressed within a liquid tube. Following this, the resin is placed within a cooled mold where compressed air is blown, which expands to the walls of the mold. One common application for this process is the creation of plastic bottles.
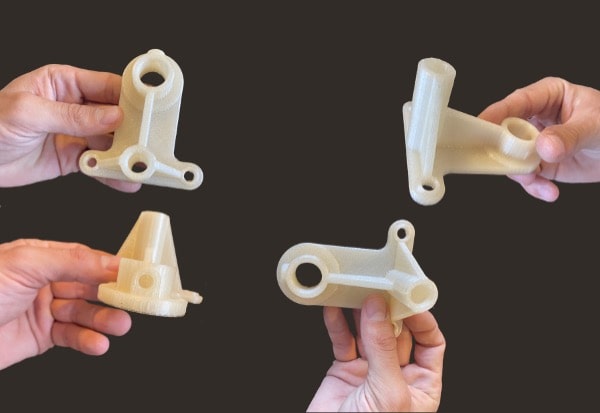
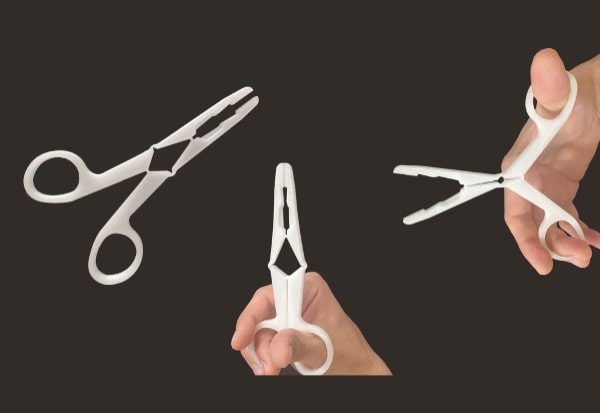
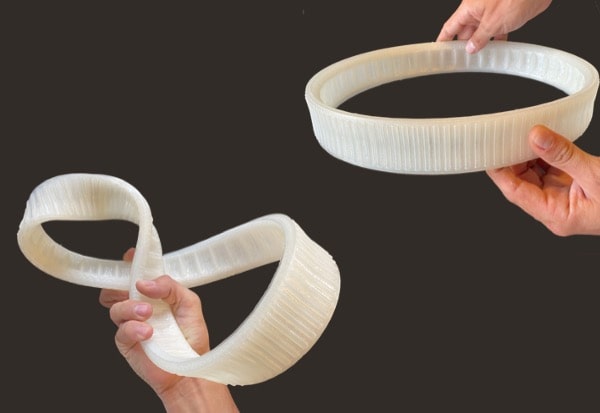
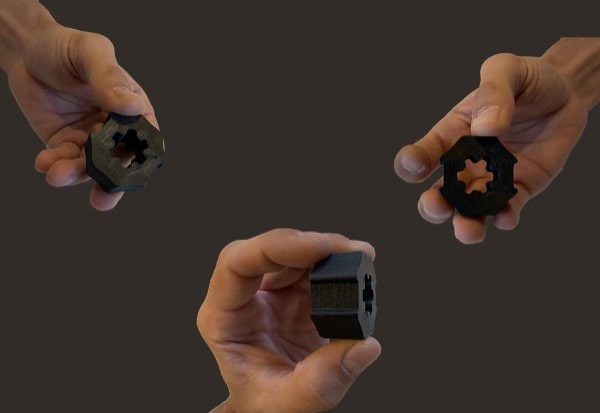
The PAM technology allows using the same material as these forming means. This results in a continuity of the material in the development cycle of a product. From prototype to series production, Pam systems accompany your project through all its phases, allowing you to use the desired material for mass production.
Let’s dive into the possibilities offered by PAM
From pellets to object, PAM technology offers the most direct process to high performances end-parts.
Metals Ceramics Commodity Elastomers Performance High Performance.


























