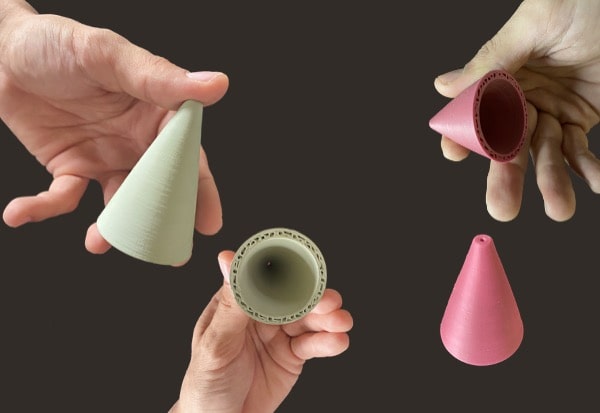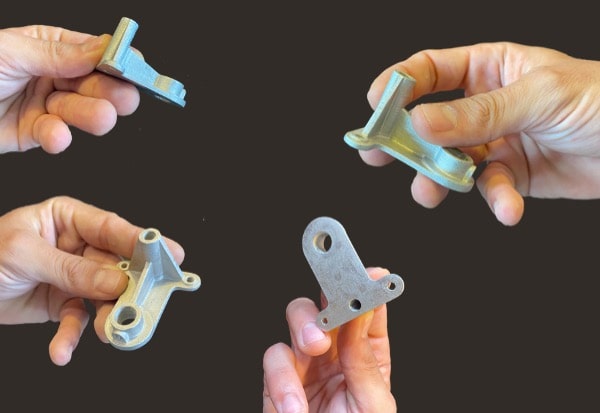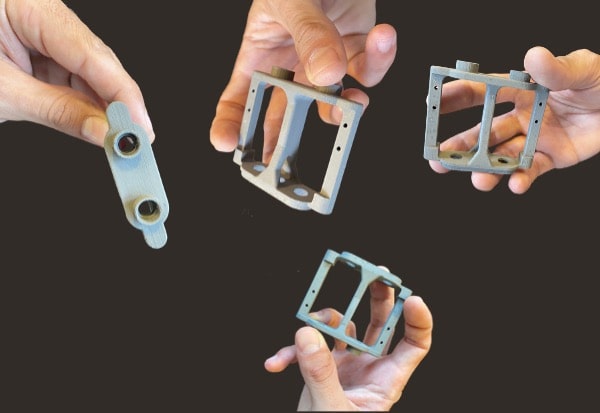
La cordiérite (2MgO.2Al2O3.5SiO2)
Cordierite ceramic, composed mainly of magnesium aluminum silicate, is widely used in applications requiring exceptional resistance to thermal shock. Thanks to its low thermal expansion coefficient, cordierite is particularly resistant to sudden changes in temperature, making it a preferred choice for high-temperature applications such as automotive catalytic converter supports, hobs and industrial ovens. In addition, it has good chemical stability, making it resistant to attack by many chemicals.
Industrial applications of cordierite include thermal insulation, refractory materials for furnaces, catalyst supports, and components for electronics and aerospace. This material is particularly effective where there are frequent temperature variations and where a combination of lightness and resistance to high temperatures is essential. In short, cordierite is a specialized material, ideal for demanding thermal environments but less suitable for applications requiring high mechanical properties.
Composition
| Component | Concentration | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| SiO2 (silicon oxide) | 50 - 55 % | Main constituent that confers thermal resistance and chemical stability. |
| Al2O3 (aluminum oxide) | 30 - 35 % | Contributes to the hardness and mechanical stability of the ceramic. |
| MgO (magnesium oxide) | 10 - 15 % | Essential for the structure of cordierite; improves resistance to thermal shock. |
| Fe2O3 (iron oxide) | < 0,5 % | Common impurity; in small quantities, it does not affect thermal properties but can alter the color. |
| CaO (calcium oxide) | < 0,1 % | Present in traces, can improve the stability of the phases under certain thermal conditions. |
Typical properties
Discover Metal and Ceramic 3D printed parts